Upper back pain can significantly impact daily activities, often radiating to the neck or mid-back. Stretching exercises, as outlined in a PDF guide, offer effective relief by improving flexibility and posture, while strengthening muscles to prevent future discomfort. Regular practice enhances mobility and reduces tension, making it essential for long-term upper back health.
1.1 Overview of Upper Back Pain and Its Impact
Upper back pain can be debilitating, often extending to the neck or mid-back and interfering with daily activities. It frequently results from muscle tightness, particularly in the latissimus dorsi and trapezius muscles. Prolonged poor posture, stress, and muscle strain exacerbate discomfort, leading to limited mobility and reduced quality of life. Addressing this issue is crucial, as neglecting it can worsen symptoms and hinder routine tasks. Understanding the causes and implementing targeted stretches can significantly alleviate pain and restore normal function. Regular exercises, as detailed in a PDF guide, provide a structured approach to managing and preventing upper back discomfort effectively.
1.2 Importance of Stretching for Upper Back Health
Stretching plays a vital role in maintaining upper back health by improving flexibility, reducing muscle tension, and enhancing posture. Regular stretching helps alleviate tightness in muscles like the trapezius and latissimus dorsi, which often contribute to pain. It also boosts blood flow, promoting healing and relaxation. Over time, consistent stretching can prevent muscle strain and improve overall mobility. Incorporating upper back stretches into your routine is essential for long-term comfort and to avoid chronic pain. A well-structured PDF guide provides easy-to-follow exercises to ensure effective and safe stretching practices for better upper back wellness.
1.3 Benefits of Using a PDF Guide for Stretching Exercises
A PDF guide offers a comprehensive and convenient resource for upper back stretching exercises. It provides detailed step-by-step instructions, images, and progress tracking to ensure effective practice. The guide is easily accessible, allowing users to follow routines anywhere without internet. It includes modifications for different fitness levels and tips for progression, making it adaptable to individual needs. Additionally, the PDF serves as a valuable reference point, helping users stay consistent and motivated in their stretching journey. This structured approach ensures that exercises are performed safely and correctly, maximizing benefits for upper back health. A free downloadable PDF is an excellent tool for achieving long-term relief and wellness.
Causes of Upper Back Pain
Upper back pain often arises from muscle strain, poor posture, and stress-related tension. These factors can lead to discomfort and stiffness, affecting daily activities and overall well-being.
2.1 Muscle Strain and Tightness
Muscle strain and tightness are common causes of upper back pain, often resulting from overuse, improper lifting, or sudden movements. Prolonged sitting or repetitive actions can lead to muscle fatigue and stiffness. Tight muscles in the shoulders and upper back can restrict movement and cause discomfort. Inactivity or lack of stretching may worsen muscle tension, making daily activities challenging. Addressing muscle strain through stretching and strengthening exercises is essential to alleviate pain and improve mobility. Regular stretching can help prevent muscle imbalances and promote long-term upper back health.
2.2 Poor Posture and Its Effects
Poor posture is a significant contributor to upper back pain, often resulting from slouching, hunching, or improper alignment of the spine. Activities like sitting at a desk, using a computer, or staring at smartphones can lead to forward head posture and rounded shoulders. Over time, this strain can cause muscle imbalances, where some muscles become overactive and others underactive. Chronic poor posture may result in discomfort, limited mobility, and even long-term structural changes, such as a curved spine or thoracic kyphosis. Addressing posture through stretching and exercises is crucial for preventing and alleviating upper back pain.
2.3 Stress-Related Tension in the Upper Back
Stress often manifests physically, leading to tension in the upper back muscles. When stressed, the body’s “fight-or-flight” response triggers muscle tightness, particularly in the neck, shoulders, and upper back. This tension can cause pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. Chronic stress may result in muscle spasms, knots, or a sensation of heaviness in the area. Activities like sitting at a desk or emotional strain can worsen this tension. Incorporating stretching exercises, deep breathing, and mindfulness practices can help alleviate stress-related upper back discomfort and promote relaxation. Addressing stress is essential for maintaining muscle health and overall well-being.
Preparing for Upper Back Stretching
Preparing for upper back stretching involves warming up, using dynamic stretches, and foam rolling to enhance flexibility and reduce muscle tension. Consulting a physiotherapist ensures safety.
3.1 Warming Up Before Stretching
Warming up is essential before starting upper back stretching exercises. It increases blood flow, reduces muscle stiffness, and prepares the body for physical activity. Begin with light cardio, such as walking or cycling, for 5-10 minutes. This promotes circulation and relaxes the muscles. Dynamic stretches, like arm circles and shoulder rolls, can also be incorporated to target the upper back and shoulders. A proper warm-up helps prevent injuries and enhances the effectiveness of stretching. Always prioritize this step to ensure a safe and productive stretching routine. Focus on gentle movements to gradually activate the muscles without overexertion.
3.2 Dynamic Stretches for Upper Back Mobility
Dynamic stretches are movements that improve upper back mobility by increasing flexibility and range of motion. Examples include arm circles, torso twists, and shoulder rolls. These exercises are performed with controlled, flowing motions and are ideal for preparing the muscles before stretching. They help reduce stiffness, enhance blood flow, and improve posture. Dynamic stretches are particularly effective for the thoracic spine and shoulder muscles. Start with slow, small movements and gradually increase intensity. Regular practice can lead to better mobility and reduced tension in the upper back region, making static stretches more effective.
3.3 Role of Foam Rolling in Flexibility
Foam rolling plays a crucial role in enhancing flexibility by releasing tension in the upper back muscles and improving circulation. It helps soften tight muscles and tendons, preparing them for stretching. Regular foam rolling can reduce muscle knots and scar tissue, allowing for better range of motion. Use a high-density foam roller to target the thoracic spine and shoulder regions. Roll slowly, focusing on areas of tension without applying excessive pressure. This technique mimics a massage, promoting relaxation and making stretching more effective. Incorporate foam rolling into your routine to improve flexibility and reduce stiffness in the upper back.
3.4 Importance of Consulting a Physiotherapist
Consulting a physiotherapist is essential for addressing upper back stiffness and pain effectively. They provide personalized assessments to identify muscle imbalances and underlying causes of discomfort. A physiotherapist can tailor stretching and strengthening exercises to your specific needs, ensuring safety and effectiveness. They also offer guidance on proper technique to avoid injury and enhance flexibility. Regular sessions can help improve posture, reduce chronic pain, and prevent future injuries. Their expertise ensures you follow a structured plan, making your upper back stretching routine more impactful and sustainable in the long term.

Best Upper Back Stretching Exercises
Discover effective stretches to relieve upper back tension, improve flexibility, and strengthen muscles. These exercises target common pain areas and promote better posture and mobility.
4.1 Cross Arm Stretch for Shoulder and Upper Back
The Cross Arm Stretch targets the shoulders and upper back, providing relief from tension and improving flexibility. To perform, pull one arm across your chest toward the opposite shoulder, holding for 20-30 seconds. Repeat on the other side. This stretch helps reduce muscle strain, enhances posture, and alleviates tightness. It’s ideal for individuals with sedentary lifestyles or those who engage in repetitive activities. Regular practice can prevent long-term discomfort and improve range of motion. Incorporate this stretch into your daily routine for lasting benefits.
4.2 Shoulder Blade Squeeze Exercise
The Shoulder Blade Squeeze targets the muscles between your shoulder blades, enhancing posture and reducing upper back tension. Sit or stand upright, place your arms at your sides, and squeeze your shoulder blades together without arching your back. Hold for 5 seconds, then release. Repeat 10-15 times. This exercise strengthens the rhomboid muscles, improving spinal alignment and reducing pain. Regular practice enhances core stability and promotes better breathing. Ideal for desk workers, it’s a simple yet effective stretch to incorporate into your daily routine for long-term upper back health benefits.
4.3 Pectoralis Stretch for Improved Posture
The Pectoralis Stretch targets tight chest muscles that contribute to rounded shoulders and poor posture. Stand in a doorway with your hands on the doorframe at shoulder height. Lean forward until you feel a stretch in your chest and shoulders. Hold for 20-30 seconds, breathing deeply. Perform 2-3 sets. Regular stretching of the pectoralis major muscle helps restore proper spinal alignment, reduces upper back strain, and improves mobility. It’s an essential exercise for individuals with desk jobs or those who frequently engage in activities that involve pushing or reaching forward.
4.4 Cat-Cow Stretch for Thoracic Mobility
The Cat-Cow Stretch is a gentle, flowing exercise that enhances thoracic spine flexibility and relieves upper back tension. Start on your hands and knees in a tabletop position. Inhale as you arch your back, lifting your head and tailbone (Cow Pose). Exhale as you round your spine, tucking your chin and pelvis (Cat Pose). Repeat for 8-10 repetitions. This stretch improves spinal mobility, reduces stiffness, and promotes better posture. It’s especially beneficial for individuals with sedentary lifestyles or those experiencing thoracic rigidity. Perform slowly, synchronizing breath with movement for maximum benefit.
4.5 Doorway Stretch for Shoulder Flexibility
The Doorway Stretch targets the shoulders and chest, improving flexibility and reducing upper back tension. Stand in a doorway with your hands on the doorframe at shoulder height. Lean forward slightly until you feel a gentle stretch across your shoulders and chest. Avoid bouncing and hold for 30 seconds. This stretch is ideal for addressing tightness from poor posture or repetitive movements. Regular practice can enhance shoulder mobility and reduce the risk of strain. It’s a simple yet effective exercise for maintaining upper back and shoulder health, especially for those with desk-based lifestyles. Consistency yields lasting results.

Strengthening Exercises for Upper Back
Strengthening exercises build muscle endurance, improve posture, and reduce upper back pain. Focus on scapular stability with bent-over rows and scapular push-ups to enhance shoulder stability and reduce strain.
5.1 Bent-Over Rows for Scapular Strength
Bent-over rows target the scapular muscles, improving upper back strength and posture. Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, bend at the hips, and grasp weights or a barbell. Keep your back straight, engage your core, and lift the weight toward your torso until your elbows are at a 90-degree angle. Lower slowly to the starting position. This exercise enhances scapular stability, reducing the risk of strain and improving overall upper back function. Proper form is crucial to avoid injury and maximize benefits for long-term strength and mobility.
5.2 Scapular Push-Ups for Shoulder Stability
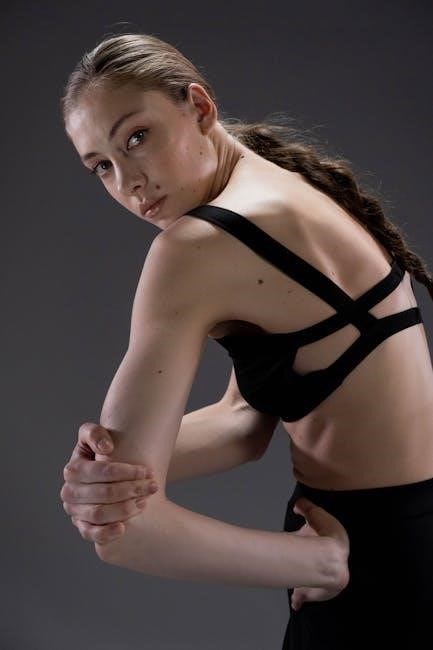

Scapular push-ups are an effective exercise for improving shoulder stability and upper back strength. Start in a plank position with your hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Engage your core, squeeze your shoulder blades together, and lower your chest slightly while maintaining a straight line from head to heels. Push back to the starting position, focusing on the scapular movement. This exercise strengthens the muscles around the shoulder blades, enhancing posture and reducing the risk of shoulder-related discomfort. Perform 8-12 repetitions for optimal results, ensuring controlled movements to avoid strain.
5.3 Superman Stretch for Thoracic Extension
The Superman Stretch targets the thoracic spine and upper back, enhancing flexibility and posture. Lie face down with arms extended forward and legs straight. Engage your core, lift your arms, chest, and legs off the ground, holding for 20-30 seconds. This stretch improves thoracic extension, relieving tightness and promoting spinal mobility. Breathe deeply, avoiding discomfort, and repeat 2-3 times. Regular practice can reduce upper back stiffness and enhance overall spinal alignment, making it ideal for those with desk-related posture issues or limited thoracic movement.

5.4 Resistance Band Exercises for Upper Back
Resistance band exercises are versatile tools for strengthening and stretching the upper back. They provide gentle to moderate resistance, making them ideal for rehabilitation or home workouts. To perform, anchor the band at shoulder height and pull it backward, squeezing your shoulder blades together. Focus on controlled movements, keeping your core engaged. Variations include rows and presses, targeting the rhomboids, trapezius, and latissimus dorsi muscles. These exercises improve posture, reduce muscle imbalances, and enhance overall upper back flexibility. Start with lighter resistance and gradually increase as strength improves for optimal results and injury prevention.

Dynamic Stretching for Upper Back
Dynamic stretching enhances upper back mobility by incorporating controlled movements. It prepares muscles for activity, improves flexibility, and reduces stiffness, promoting better range of motion and posture.
6.1 Arm Circles for Shoulder Mobility
Arm circles are a dynamic stretch that targets the shoulders and upper back, improving mobility and flexibility. Stand tall with arms extended sideways at shoulder height. Make small circles forward for 10-15 repetitions, then switch direction. Gradually increase the size of the circles as your shoulders loosen. This exercise helps reduce stiffness, enhances joint mobility, and prepares the muscles for more intense movements. Regular practice can improve posture and reduce the risk of injury. Incorporate arm circles into your routine for a stronger, more flexible upper back. Smooth, controlled movements are key for maximum benefit.
6.2 Side-to-Side Neck Stretches
Side-to-side neck stretches target the muscles connecting the neck and upper back, enhancing flexibility and relieving tension. Sit or stand with good posture, then gently tilt your head to the right, bringing your ear toward your shoulder. Hold for a few seconds before returning to center. Repeat on the left side. Perform 8-10 repetitions on each side, focusing on smooth, controlled movements. This stretch helps reduce muscle tightness, improves range of motion, and alleviates stress-related neck pain. Regular practice promotes better posture and reduces the risk of upper back strain. Breathe naturally and avoid forcing your head beyond a comfortable range.
6.3 Thoracic Spine Rotations
Thoracic spine rotations are essential for improving mobility and reducing stiffness in the upper back. Sit or stand tall, place your hands behind your back, and gently rotate your torso to one side while keeping your hips still. Hold for a few seconds, then slowly return to center. Repeat on the opposite side. This exercise helps enhance flexibility, reduce muscle tension, and improve posture. Perform 8-10 repetitions on each side, focusing on controlled movements. Regular practice can alleviate upper back pain and improve overall spinal alignment. Breathe naturally and avoid forcing the rotation beyond a comfortable range.
6.4 Shoulder Rolls and Chest Openers
Shoulder rolls and chest openers are dynamic stretches that target the upper back and shoulder muscles. Start with shoulder rolls: roll your shoulders forward and upward in a circular motion, then reverse the direction. Repeat for 8-10 repetitions. For chest openers, stand in a doorway with your hands on the doorframe at shoulder height. Lean forward, stretching your chest and shoulders while keeping your arms straight. Hold for 20-30 seconds and breathe deeply. These exercises improve posture, reduce tension, and enhance mobility in the upper back region. Perform them slowly and avoid bouncing to maximize benefits and prevent strain.

Tips for an Effective Stretching Routine
Consistency and patience are key. Always warm up beforehand and focus on smooth, controlled movements. Incorporate deep breathing to enhance relaxation and avoid forcing stretches beyond comfort.
7;1 Frequency and Duration of Stretching Sessions
Aim to stretch 3-4 times weekly for optimal results. Sessions should last 15-20 minutes, focusing on 2-3 key exercises per session. Start with shorter durations and gradually increase as flexibility improves. Consistency is crucial for long-term benefits. For acute discomfort, daily stretching may be beneficial, but avoid overstretching. Listen to your body and adjust frequency based on individual needs and progress. Regularity combined with proper technique ensures sustained improvement in upper back flexibility and posture.
7.2 Breathing Techniques During Stretches
Proper breathing enhances relaxation and reduces tension during upper back stretches. Practice deep belly breathing: inhale deeply through your nose, allowing your abdomen to rise, then exhale slowly through your mouth. Exhale as you move into the stretch to release muscle tension. Avoid holding your breath, as it can increase stiffness. Maintain a steady rhythm, breathing naturally and smoothly. This technique improves oxygen flow, reduces discomfort, and maximizes the effectiveness of each stretch. Consistent breathing practice will help you stay focused and ensure a safe, beneficial stretching routine.
7.3 Avoiding Pain During Stretching
To ensure a safe and effective stretching routine, prioritize pain-free movements. If a stretch causes sharp pain, stop immediately and modify the exercise. Gentle stretching within a comfortable range prevents injury. Avoid bouncing or forcing your body beyond its limits, as this can strain muscles. Focus on controlled, gradual movements to maintain joint stability. Use props like pillows or blocks for support if needed. If pain persists, consult a healthcare professional to rule out underlying issues. Remember, stretching should relieve tension, not cause discomfort.
7.4 Progressing Your Stretching Routine
As you advance in your stretching journey, gradually increase intensity by holding stretches longer or deepening the stretch slightly. Incorporate variations of exercises to target different muscle groups. Introduce dynamic stretches or resistance bands for added challenge. Monitor progress by noting improvements in flexibility and posture. Adjust routines every few weeks to avoid plateaus and keep the body engaged. Incorporate new exercises or techniques to maintain motivation. Always prioritize proper form and listen to your body to ensure safe progression. This systematic approach ensures continuous improvement in upper back flexibility and overall posture.

Improving Posture Through Stretching
Stretching helps correct rounded shoulders and slouching by targeting tight chest muscles and strengthening weak upper back muscles. Regular practice promotes spinal alignment and stability for better posture.
8.1 Exercises to Correct Rounded Shoulders
Correcting rounded shoulders involves stretching tight chest muscles and strengthening weak upper back muscles. Exercises like chest stretches and shoulder blade squeezes help improve posture. Regular practice of these stretches can reduce shoulder hunching and promote proper spinal alignment. Incorporating exercises like arm circles and thoracic rotations can also enhance mobility and reduce muscle imbalances. Consistency in performing these exercises, along with proper form, is key to achieving long-term postural improvement and preventing further discomfort or injury.
8.2 Stretching for a Straighter Spine
Stretching for a straighter spine focuses on improving flexibility and reducing muscle tension in the thoracic region. Exercises like the child’s pose and cat-cow stretch help elongate the spine and enhance mobility. Additionally, stretches targeting the chest and shoulders, such as the doorway stretch, can help counteract forward-leaning postures. Regular stretching promotes better spinal alignment, reducing the curvature of the upper back. Consistent practice, combined with proper breathing techniques, can lead to a more upright and balanced posture over time.
8.3 Strengthening Core Muscles for Better Posture
Strengthening core muscles is essential for maintaining better posture, as they provide stability to the spine and pelvis. Exercises like planks, bird-dog, and pelvic tilts target the abdominals and lower back, improving spinal alignment. A strong core helps reduce strain on the upper back by promoting a neutral spine position. Incorporating core-strengthening exercises into your routine can enhance posture and reduce the risk of muscle imbalances. Combine these with stretching for a holistic approach to achieving and maintaining a straighter, healthier spine.
Downloadable PDF Guide Features
Our downloadable PDF guide offers customizable workout plans, step-by-step instructions, and clear images. It includes expert tips for progression and modifications to suit all fitness levels.
9.1 Comprehensive Exercise Plans
The PDF guide provides detailed, structured routines tailored to address upper back stiffness and pain. Each plan targets specific muscle groups, offering a mix of stretching and strengthening exercises. Variations are included to suit different fitness levels, ensuring accessibility for beginners and challenging options for advanced users. The exercises are organized progressively, focusing on improving posture, reducing muscle tension, and enhancing mobility. Clear goals and outcomes are outlined for each routine, helping users track their progress effectively. Whether you’re recovering from injury or maintaining wellness, these plans offer a balanced approach to achieving long-term upper back health and flexibility.
9.2 Step-by-Step Instructions and Images
The PDF guide includes detailed step-by-step instructions for each exercise, ensuring clarity and ease of understanding. High-quality images or diagrams accompany each movement, providing visual guidance to help users maintain proper form and alignment. These visuals are especially helpful for beginners, allowing them to follow along with confidence. Each step is clearly explained, focusing on key movements, breathing techniques, and proper posture. The combination of instructions and images ensures that users can perform the stretches safely and effectively, making the guide accessible for all skill levels and promoting consistent progress in upper back flexibility and strength.
9.3 Progress Tracking and Modification Tips
The PDF guide offers tools for tracking progress, allowing users to monitor improvements in flexibility and strength over time. Modification tips are provided for each exercise, catering to different fitness levels and abilities. Users can adjust the intensity or difficulty as they progress, ensuring continuous challenge and growth. The guide also includes advice on when to increase or modify stretches based on individual needs. This feature helps users stay motivated and tailor their routine for optimal results, making the guide adaptable and effective for long-term upper back health and wellness.
Upper back stretching exercises are essential for reducing pain, improving posture, and enhancing mobility. Consistency is key to achieving long-term benefits and maintaining a healthy upper back.

10.1 Long-Term Benefits of Upper Back Stretching
Regular upper back stretching offers numerous long-term benefits, including improved posture, reduced muscle tension, and increased mobility. It strengthens the muscles, preventing future strain and enhancing overall well-being. Consistent practice can alleviate chronic pain, promote better spinal alignment, and boost flexibility. Over time, these exercises help maintain a healthy upper back, reducing the risk of injuries and improving daily activities. Incorporating stretching into your routine can lead to a stronger, more balanced physique and a higher quality of life. A downloadable PDF guide provides a structured approach to achieving these lasting benefits through targeted exercises.
10.2 Encouragement to Start Your Stretching Journey
Embrace the transformative power of upper back stretching by taking the first step today. Every small effort counts, and consistency will lead to remarkable improvements in your posture, strength, and overall well-being. Discover how these exercises can empower you to tackle daily tasks with renewed energy and confidence. The journey may seem daunting at first, but with a structured guide like a downloadable PDF, you’ll have all the tools needed to succeed. Start now, and let each stretch bring you closer to a healthier, pain-free life. Your body will thank you for the commitment to its care.
